This page explains how to configure Admission Controllers in the Kubermatic Kubernetes Platform.
How do I turn on an admission controller?
The Kubermatic Kubernetes Platform manages the Kubernetes API server by setting the enable-admission-plugins flag with a comma-delimited
list of admission control plugins to be enabled during cluster creation.
In the current version, the default ones are:
NamespaceLifecycle
NodeRestriction
LimitRanger
ServiceAccount
DefaultStorageClass
DefaultTolerationSeconds
MutatingAdmissionWebhook
ValidatingAdmissionWebhook
Priority
ResourceQuota
Supported Additional Admission Plugins
The Kubermatic Kubernetes Platform also provides support for three additional plugins that can be enabled if needed:
PodNodeSelectorPodSecurityPolicyEventRateLimit
They can be selected in the UI wizard.
PodNodeSelector Configuration
Selecting the PodNodeSelector plugin expands an additional view for the plugin-specific configuration.
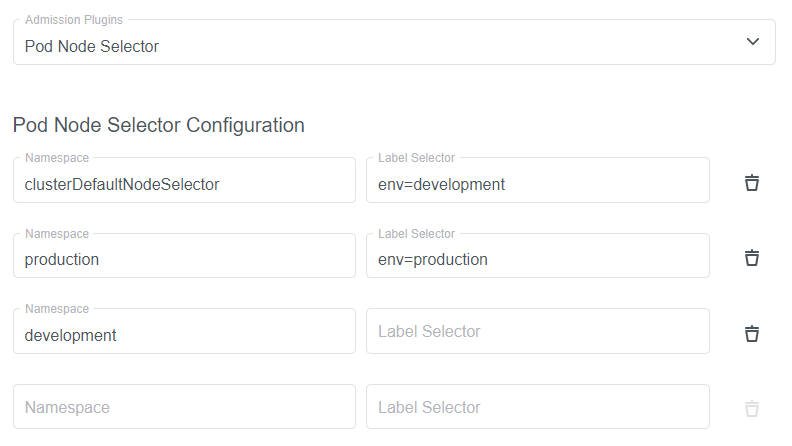
In this view you can define selector for namespaces that have no label selector specified. This example defines the default
NodeSelector for the cluster, as well as whitelist for each namespace.
Every pod created in the production namespace will be injected the NodeSelector env=production
Every pod in the development namespace will inherit the clusterDefaultNodeSelector, in this case env=development.
EventRateLimit Configuration
EventRateLimit is an admission plugin that sets up limits for Events being published to the Kubernetes API. KKP supports setting up limits on a per-namespace basis so no namespace can overwhelm the Kubernetes API with a high number of events.
Selecting the EventRateLimit plugin expands an additional view for the plugin-specific configuration.
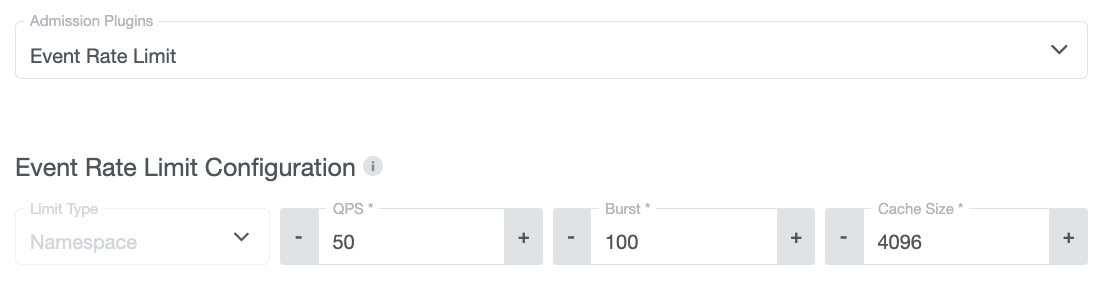
The available fields for the configuration are:
- QPS: The allowed “queries per second”. This determines whether an incoming
Eventrequest is allowed or not for the respective bucket (in this case, buckets are created per namespace) within one second if the burst budget is exhausted. Unused QPS are added to the burst budget. Defaults to50. - Burst: The maximum allowed events created within a second. Once the burst budget is exhausted, the QPS determine whether an
Eventis accepted or not. Each second, the unused QPS are added back to the budget, up to the limit set by this field. Defaults to100. - Cache Size: The number of buckets that are stored in an LRU cache. If a bucket is removed from the cache because it is not used for any request, the next request for it will reset the bucket’s burst budget and add it back to the LRU cache. Defaults to
4096.
Custom Admission Plugins
In addition to the admission plugins enabled by default or enabled as a managed KKP feature, KKP supports adding a list of admission plugins through the KKP API. This is limited to admission plugins that do not need additional configuration files or flags passed to the Kubernetes API server, for example AlwaysPullImages or SecurityContextDeny (which is recommended if there is no security policy enforcement (PSPs or OPA Gatekeeper) in the cluster).
Custom admission plugins cannot be validated by KKP and there is a risk of unintended consequences when enabling some admission plugins. Make sure you test and validate your list of admission plugins on test user clusters before enabling them on production environments.
This can achieved by setting or updating the field spec.admissionPlugins in the API for cluster resources. This field is a list, so it would look something like this:
spec:
admissionPlugins:
- AlwaysPullImages
- SecurityContextDeny