Add EKS Cluster
You can add an existing Kubernetes cluster and then manage it using KKP.
From the Clusters page, click External Clusters. Click the Add External Cluster button and pick Elastic Kubernetes Engine provider.
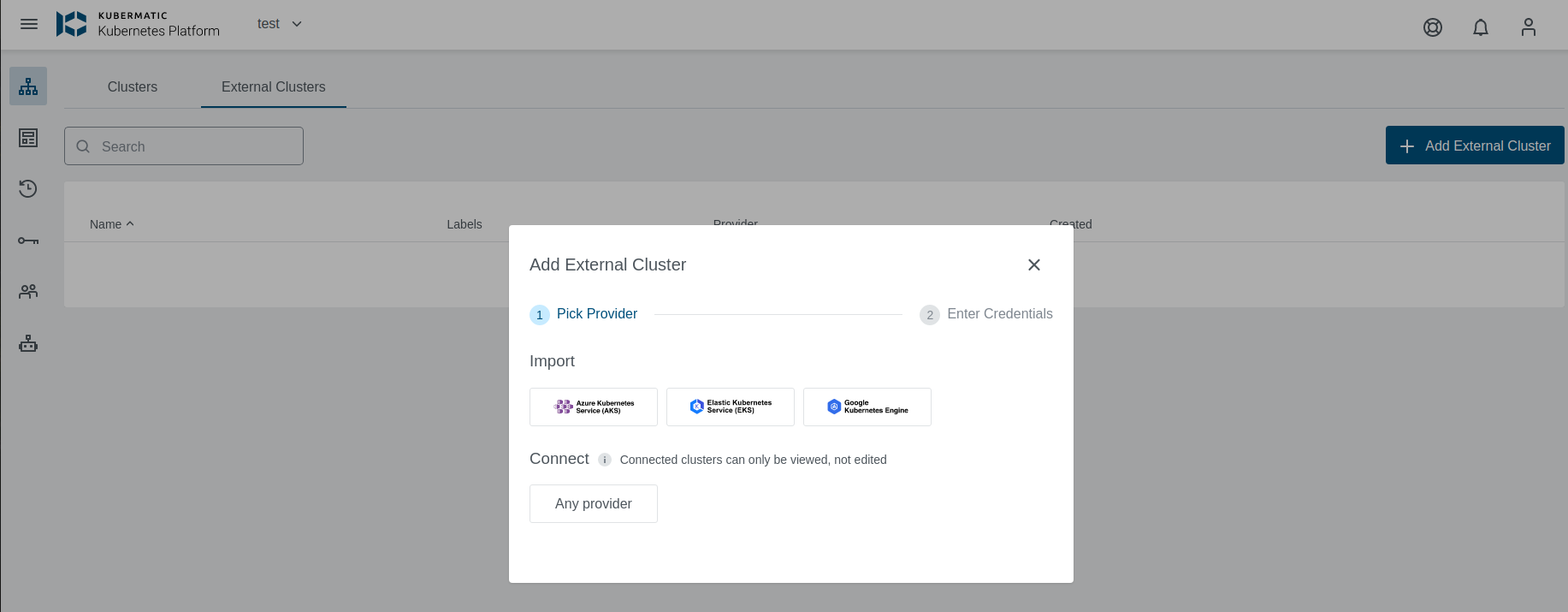
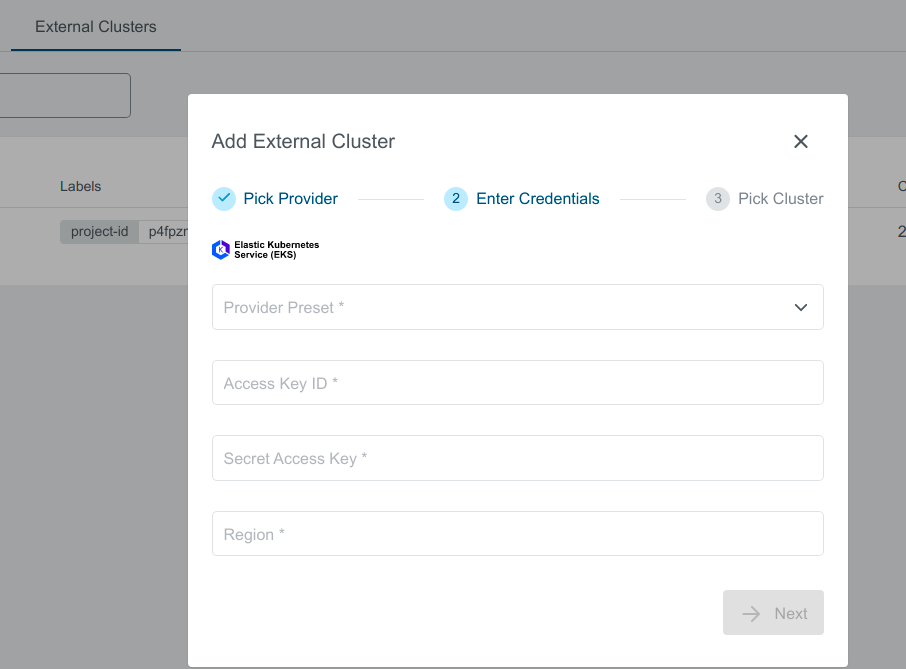
Select preset with valid credentials or enter EKS Access Key ID, Secret Access Key , and Region to connect to the provider.
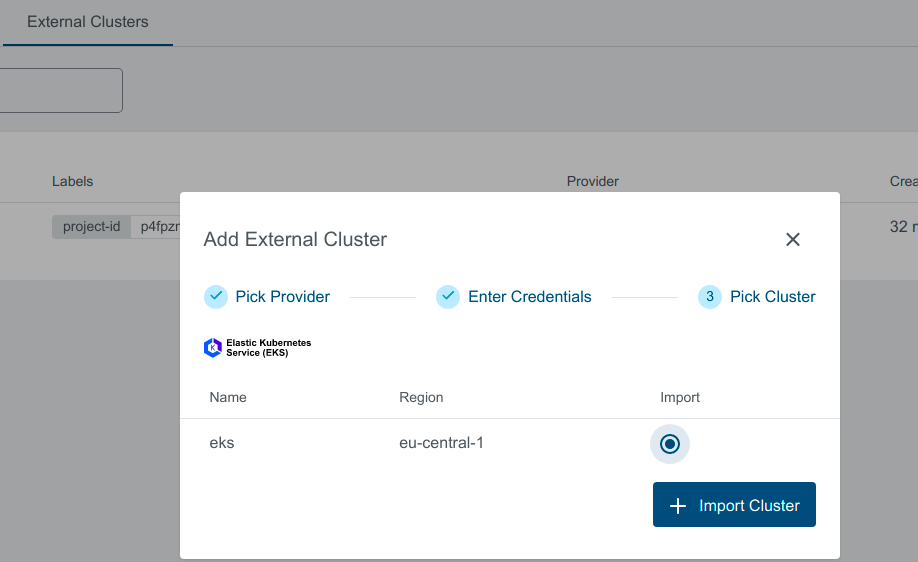
You should see the list of all available clusters in the region specified. Select the one and click the Import Cluster button. Clusters can be imported only once in a single project. The same cluster can be imported for the other projects.
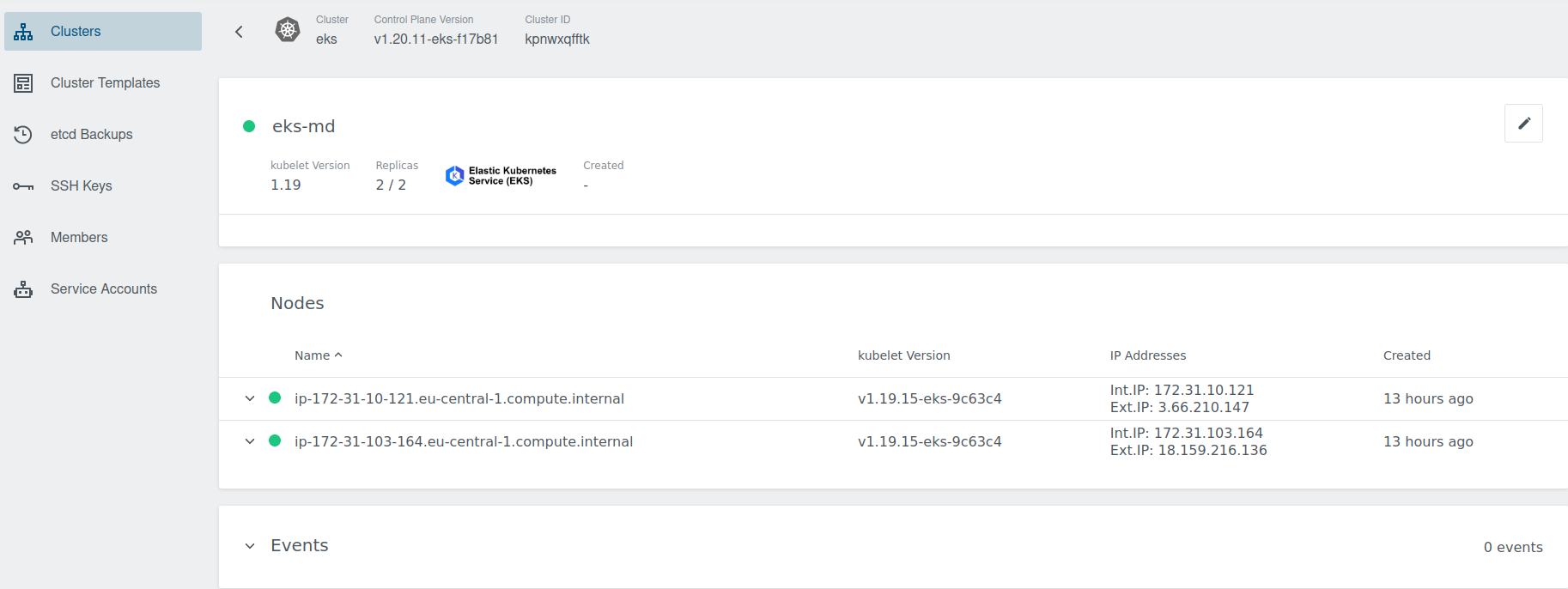
Cluster Details Page
After the cluster is added, the KKP controller retrieves the cluster kubeconfig to display all necessary information.
A healthy cluster has Running state. Otherwise, the cluster can be in the Error state. Move the mouse cursor over the state indicator to get more details.
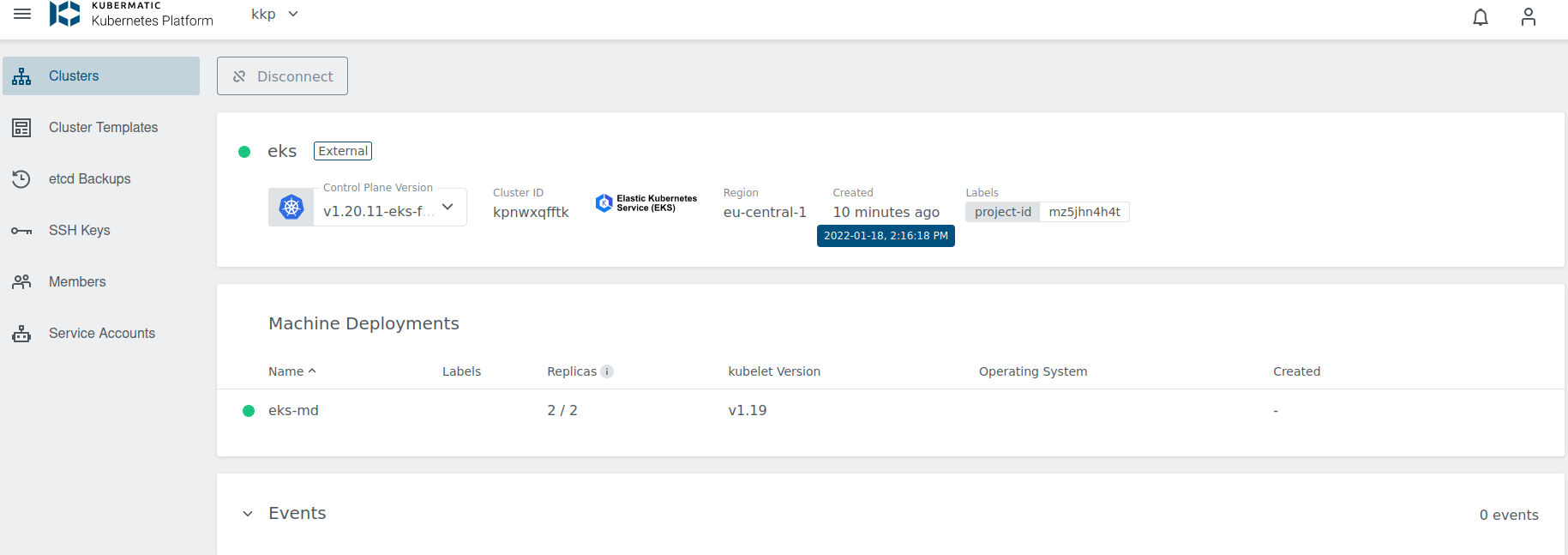
You can also click on Machine Deployments to get the details:
Update Cluster
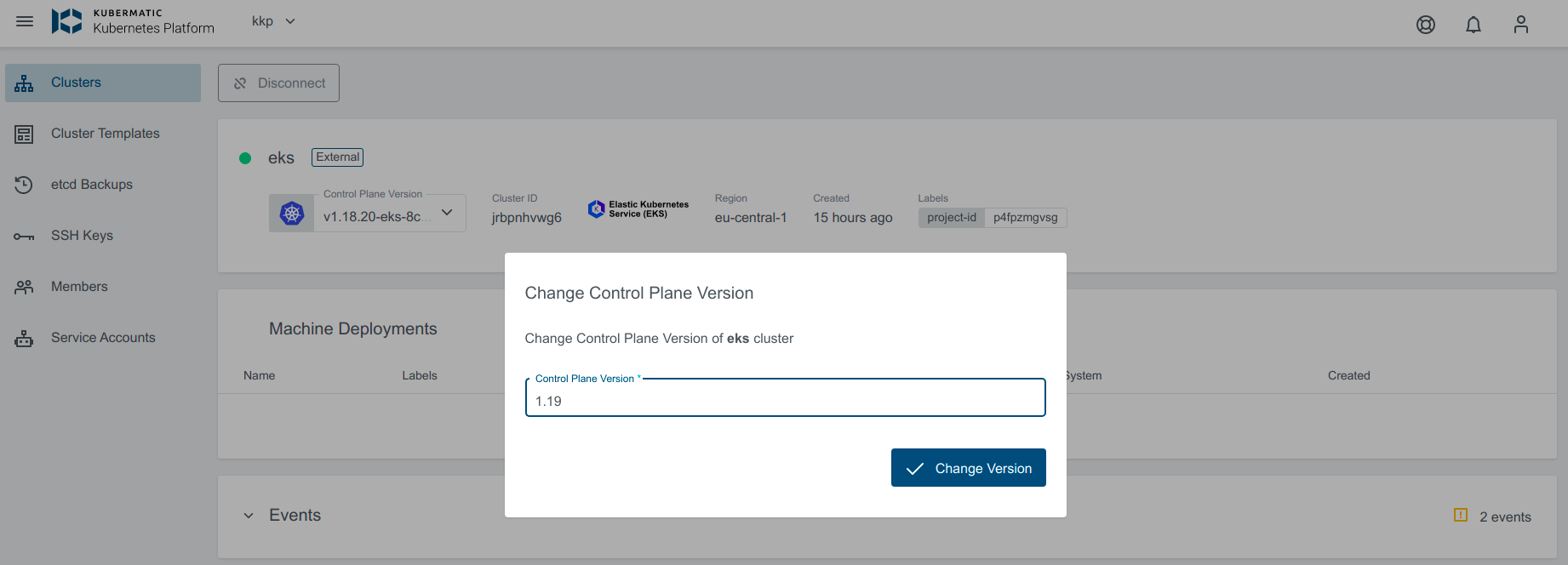
Upgrade Version
To upgrade, click on the little dropdown arrow beside the Control Plane Version on the cluster’s page and specify the version. For more details about EKS available Kubernetes versions
Amazon EKS Kubernetes versions
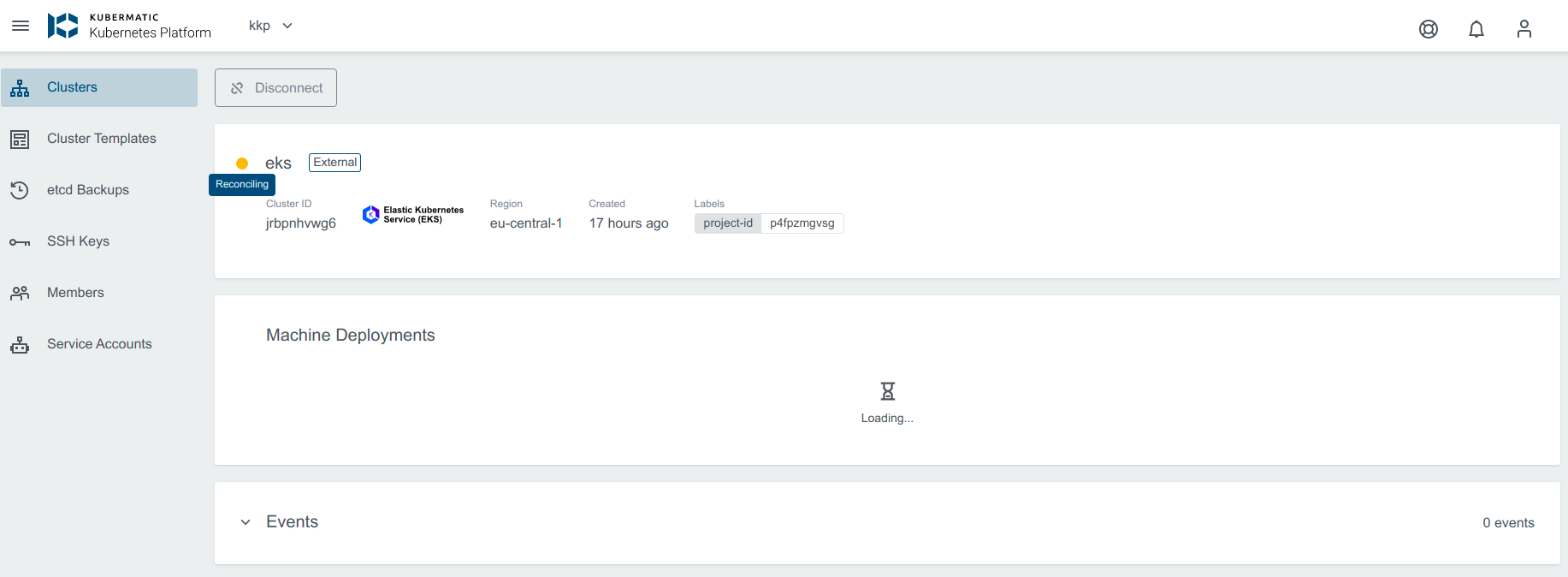
If the upgrade version provided is valid, the cluster state will change to Reconciling
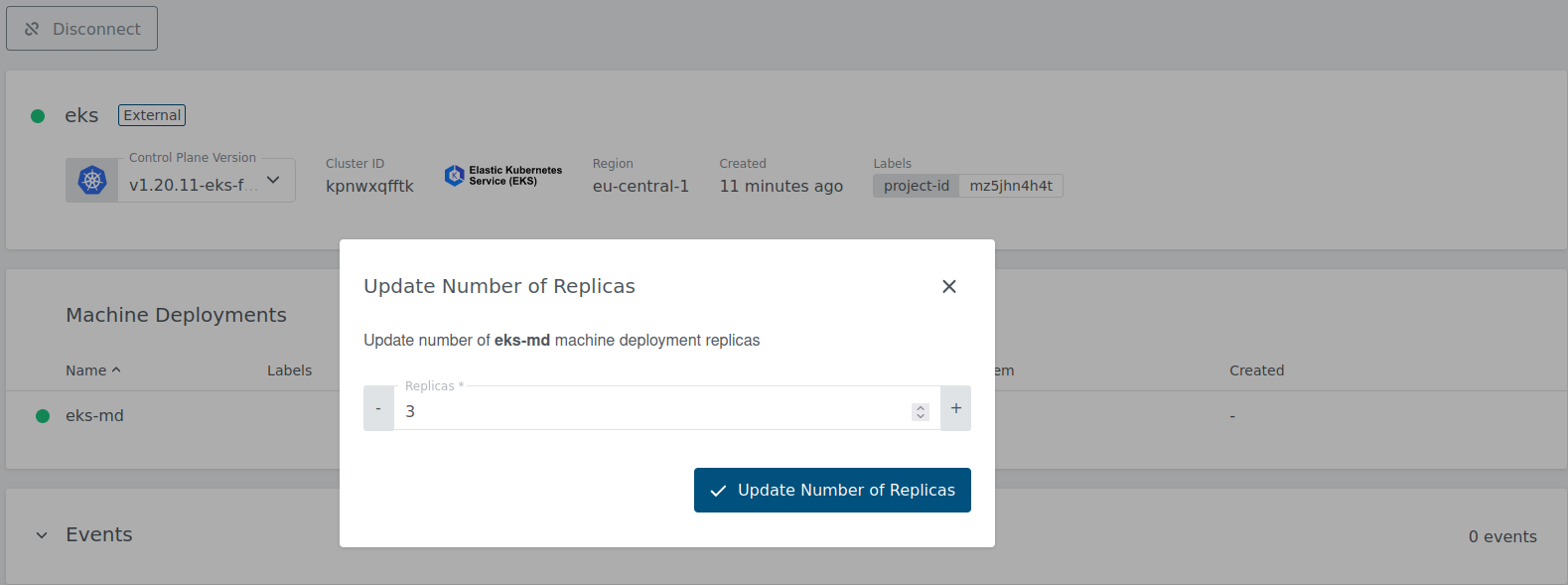
Scale the Machine Deployment
Navigate to the cluster overview, scroll down to machine deployments and click on the edit icon next to the machine deployment you want to edit.
In the popup dialog, you can now increase or decrease the number of worker nodes that are managed by this machine deployment.
Either specify the number of desired nodes or use the + or - to increase or decrease node count.
Authenticating with EKS
The KKP platform allows getting kubeconfig file for the EKS cluster. The end-user must be aware that the kubeconfig expires after some short period of time. It’s recommended to create your kubeconfig file with the AWS CLI.
Configure AWS credentials
The AWS CLI uses credentials and configuration settings located in multiple places, such as the system or user environment variables, local AWS configuration files, or explicitly declared on the command line as a parameter.
The AWS CLI stores sensitive credential information that you specify with aws configure in a local file named credentials,
in a folder named .aws in your home directory. The less sensitive configuration options that you specify with aws configure
are stored in a local file named config, also stored in the .aws folder in your home directory.
Example:
~/.aws/credentials
[default]
aws_access_key_id=AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE
aws_secret_access_key=wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY
Create kubeconfig file
Now you can create kubeconfig file automatically using the following command:
aws eks update-kubeconfig --region region-code --name cluster-name
By default, the resulting configuration file is created at the default kubeconfig path (.kube/config) in your home directory
or merged with an existing kubeconfig file at that location. You can specify another path with the --kubeconfig option.