Audit Logging is one of the key security features provided by Kubernetes. Once enabled in the Kubernetes API server, it provides a chronological record of operations performed on the cluster by users, administrators and other cluster components.
Audit logging is also a key requirement of the Kubernetes CIS benchmark.
For more details, you can refer to the upstream documentation.
Kubermatic Kubernetes Platform (KKP) Support
KKP provides two levels of support for the Audit Logging:
- Audit Logging on user-cluster level
- Audit Logging on a datacenter level
Kubernetes Audit Logging is optional and is not enabled by default, since it requires additional memory and storage resources, depending on the specific configuration used.
Audit logs, if enabled, are emitted by a sidecar container called audit-logs in the kubernetes-apiserver Pods on the Seed Cluster in your cluster namespace. Setting up the MLA stack on Master / Seed will allow storing the audit logs alongside other Pod logs collected by the MLA stack.
if you do not choose an audit policy preset, KKP will set up a minimal audit policy for you.
This file is stored in a ConfigMap named audit-config on the Seed Cluster in your cluster namespace. To modify the default policy, you can edit this ConfigMap using kubectl:
$ kubectl edit -n cluster-<YOUR CLUSTER ID> configmap audit-config
apiVersion: audit.k8s.io/v1
kind: Policy
rules:
- level: Metadata
Audit Policy Presets
KKP supports a set of maintained audit policies as presets in case you do not want to tune the audit policy for yourself.
A preset can be selected during cluster creation in the UI or by setting the field auditLogging.policyPreset on a
user-cluster spec (when audit logging is enabled). The preset selection can be unset by setting the field to an empty string.
Enabling an audit policy preset on your user-cluster will override any manual changes to the audit-config ConfigMap.
The following presets are available right now:
metadata: Logs metadata for any request (matches the default policy configured when using no policy preset)minimal: Is considered the bare minimum that allows to audit for key operations on the cluster. Logs the following operations:- any modification to
Pods,Deployments,StatefulSets,DaemonSetsandReplicaSets(complete request and response bodies) - any access to Pods via shell (by using
execto spawn a process) or port-forwarding/proxy (complete request and response bodies) - access to container logs (metadata only)
- any access (read, write or delete) to
SecretsandConfigMaps(metadata only, as the request body could include sensitive information)
- any modification to
recommended: Logs everything inminimalplus metadata for any other request. This is the most verbose audit policy preset, but is recommended due to its extended coverage of security recommendations like the CIS Benchmark
User-Cluster Level Audit Logging
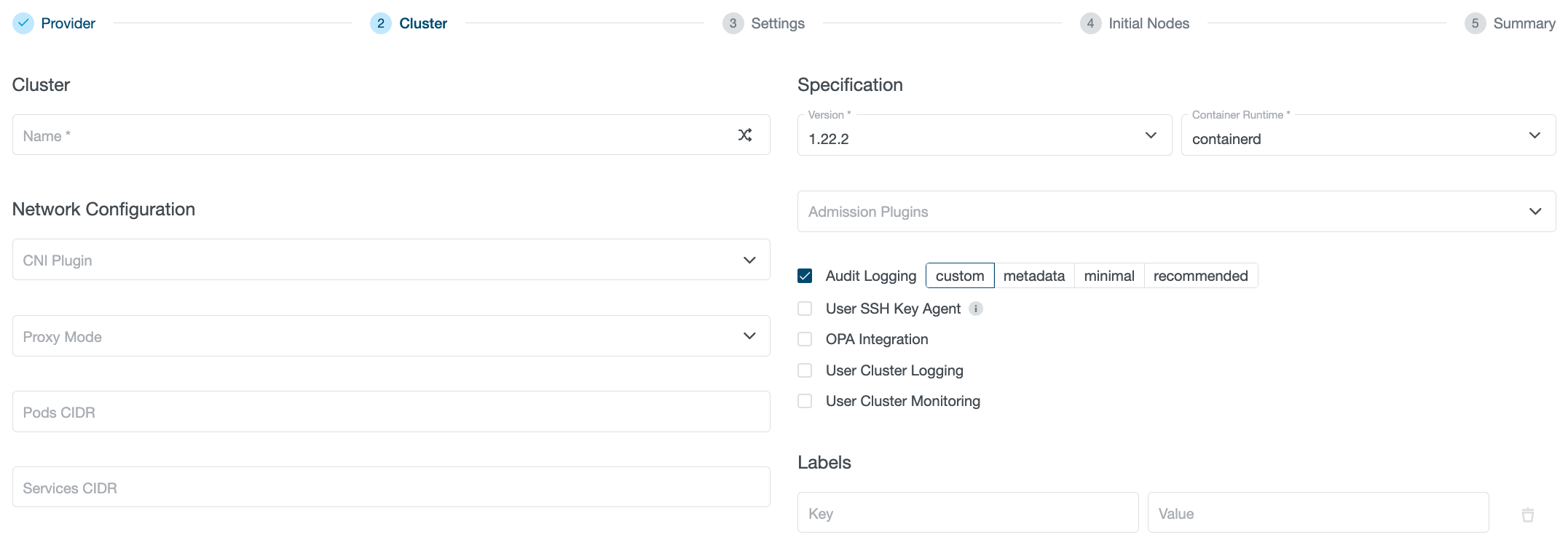
To enable user-cluster level Audit Logging, simply check Audit Logging in the KKP dashboard Create Cluster page. You can either select “custom” to be able to edit the ConfigMap for audit logging later on or set your cluster up with a preset:
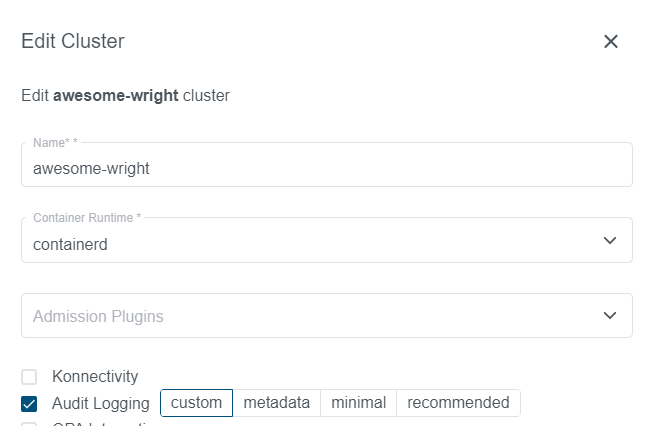
For exiting clusters, you can go to the cluster page, edit your cluster and enable (or disable) Audit Logging:
Datacenter Level Audit Logging
KKP also supports enabling Audit Logging on the datacenter level. In this case, the option is enforced on all user-clusters in the datacenter. The user-cluster level flag is ignored in this case.
To enable this, you will need to edit your datacenter definitions in a Seed, and set enforceAuditLogging to true in the datacenter spec.