Share Clusters via Delegated OIDC Authentication Overview
The purpose of this feature is to allow using an OIDC provider like dex to authenticate to a Kubernetes cluster
managed by Kubermatic Kubernetes Platform (KKP). This feature can be used to share access to a cluster with other users.
How Does It Work?
This section will demonstrate how to obtain and use the kubeconfig to connect to a cluster owned by a different user.
Note that the user to which the kubeconfig is shared will not have any permissions inside that shared cluster unless
explicitly granted by creating appropriate RBAC bindings.
In order to demonstrate the feature we are going to need a working cluster. If you don’t have one please check the how to create a cluster section. If the feature was enabled on your installation you will see a “Share cluster” button after navigating to “Cluster details” page.
Right after clicking on the button you will see a modal window where you can copy the generated link to your clipboard.

You can now share this link with anyone that can access the KKP UI. After login, that person will get a download link for a
kubeconfig.
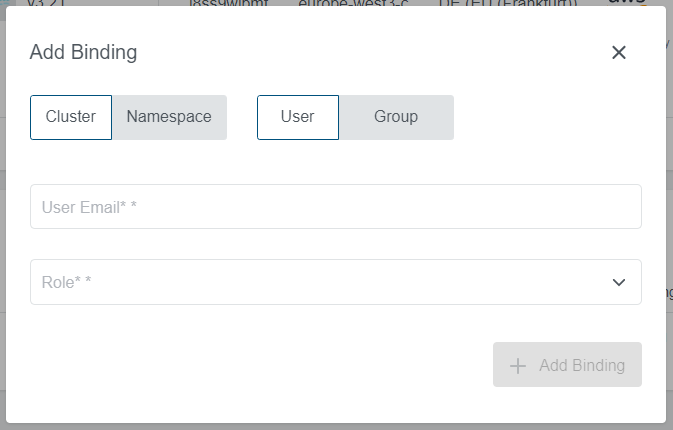
In order for the shared kubeconfig to be of any use, we must grant that other user some permissions. To do so, configure
kubectl to point to the cluster and create a rolebinding or clusterrolebinding, using the email address of the user
the kubeconfig was shared to as value for the user property.
The following example command grants read-only access to the cluster to user@example.com:
kubectl create clusterrolebinding exampleuserviewer --clusterrole=view --user=user@example.com
Now it’s time to let the user the cluster was shared to use the config and list some resources for example pods.
Even though there might be no pods running at the moment the command will not report any authorization related issues.
kubectl get pods
#No resources found.
If the exampleuserviewer binding gets deleted or something else goes wrong, the following output is displayed instead:
kubectl get pods
#Error from server (Forbidden): pods is forbidden: User "user@example.com" cannot list pods in the namespace "default"
Prerequisites
In order to enable the feature the necessary flags must be passed to various applications.
KKP needs to be reconfigured by adjusting the KubermaticConfiguration. In the auth.spec section, more fields
need to be specified. In addition to this, two feature flags need to be set.
apiVersion: operator.kubermatic.io/v1alpha1
kind: KubermaticConfiguration
metadata:
# ...
spec:
featureGates:
# exposes an HTTP endpoint for generating kubeconfig
# for a cluster that will contain OIDC tokens
OIDCKubeCfgEndpoint:
enabled: true
# configures the flags on the API server to use
# OAuth2 identity providers
OpenIDAuthPlugin:
enabled: true
ui:
# enable shared kubeconfig feature in the dashboard
config: |-
{
"share_kubeconfig": true
}
auth:
# This is the OIDC issuer client ID and defaults to
# "<spec.auth.clientID>Issuer". As the default issuer used
# for the dashboard is "kubermatic", this defaults to:
issuerClientID: kubermaticIssuer
# The shared secret between Dex and KKP. This needs to be
# randomly generated, e.g. via
# cat /dev/urandom | tr -dc A-Za-z0-9 | head -c32
issuerClientSecret: ""
# used for encrypting HTTP cookies, also needs to be
# randomly generated
issuerCookieKey: ""
# This is the OIDC redirect URL and defaults to the
# kubeconfig endpoint in the dashboard, i.e.
# "https://<spec.ingress.domain>/api/v1/kubeconfig"
issuerRedirectURL: https://example.com/api/v1/kubeconfig
# OIDC provider's root CA certificates chain, see
# the section further down in this document for more
# information on how to generate this
caBundle: |-
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
....
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
These values must match the configuration used for the oauth Helm chart (Dex). Define
the new issuerClientID in Dex by editing your values.yaml used for setting Dex up:
dex:
clients:
- id: kubermaticIssuer
name: Kubermatic OIDC Issuer
secret: "" # put the value of issuerClientSecret here
RedirectURIs:
- https://example.com/api/v1/kubeconfig # issuerRedirectURL
Root CA Certificates Chain
In order to verify OIDC provider’s certificate in kubermatic-controller-manager when establishing
TLS connection, a public root CA certificate is required. Ideally the whole chain including all intermediate
CAs certificates is included. Note that we expect that all certificates will be PEM encoded.
For example if the certificate used by your provider was issued by Let’s Encrypt. You can visit Let’s Encrypt to download the necessary certificates and use the following command to prepare the bundle.
cat isrgrootx1.pem.txt lets-encrypt-x3-cross-signed.pem.txt > caBundle.pem
This bundle must then be copied verbatim into the KubermaticConfiguration.
Update KKP
After all values are set up, it’s time to update the KKP master cluster. Update the oauth chart first:
Helm 3
helm --namespace oauth upgrade --install --wait --values values.yaml oauth charts/oauth/
Now that the issuer is available, update the KubermaticConfiguration:
kubectl -n kubermatic apply -f kubermaticconfig.yaml
After the operator has reconciled the KKP installation, OIDC auth will become available.
Role-Based Access Control Predefined Roles
KKP provides predefined roles and cluster roles to help implement granular permissions for specific resources
and to simplify access control across the user cluster. All of the default roles and cluster roles are labeled
with component=userClusterRole.
| Default ClusterRole | Description |
|---|---|
| admin | Allows admin access. allows read/write access to most resources in a namespace, including the ability to create roles and role bindings within the namespace. This role does not allow write access to resource quota or to the namespace itself. |
| edit | Allows read/write access to most objects in a namespace. This role does not allow viewing or modifying roles or role bindings. However, this role allows accessing secrets and running pods as any service account in the namespace |
| view | Allows read-only access to see most objects in a namespace. It does not allow viewing roles or role bindings. |
| Default Role | Description |
|---|---|
| namespace-admin | Allows admin access. Allows read/write access to most resources in a namespace. |
| namespace-editor | Allows read/write access to most objects in a namespace. This role allows accessing secrets and running pods as any service account in the namespace |
| namespace-viewer | Allows read-only access to see most objects in a namespace. |
The cluster owner is automatically connected to the admin cluster role.
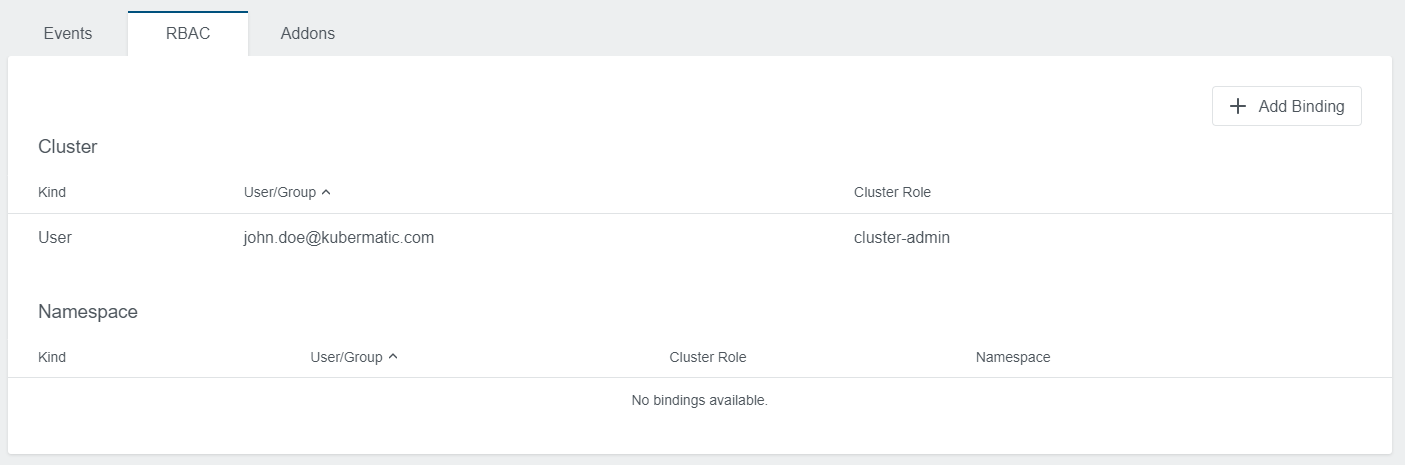
The project user with owner and editor privileges can add and remove bindings to existing roles and cluster roles.