This manual explains how to manage KKP global settings such as custom links, displayed distributions and others.
It can be done from the UI and also from the command line with kubectl.
Accessing the Admin Panel
Admin panel can be accessed only by logged in users that have administrator privileges. You can check and edit them
using kubectl:
$ kubectl get user -o=custom-columns=INTERNAL_NAME:.metadata.name,NAME:.spec.name,EMAIL:.spec.email,ADMIN:.spec.admin
$ kubectl edit user ...
Admin privileges can be granted for users also from the admin panel in the UI. To access the admin panel click the
Admin Panel entry in the user menu:
Admin Panel Overview
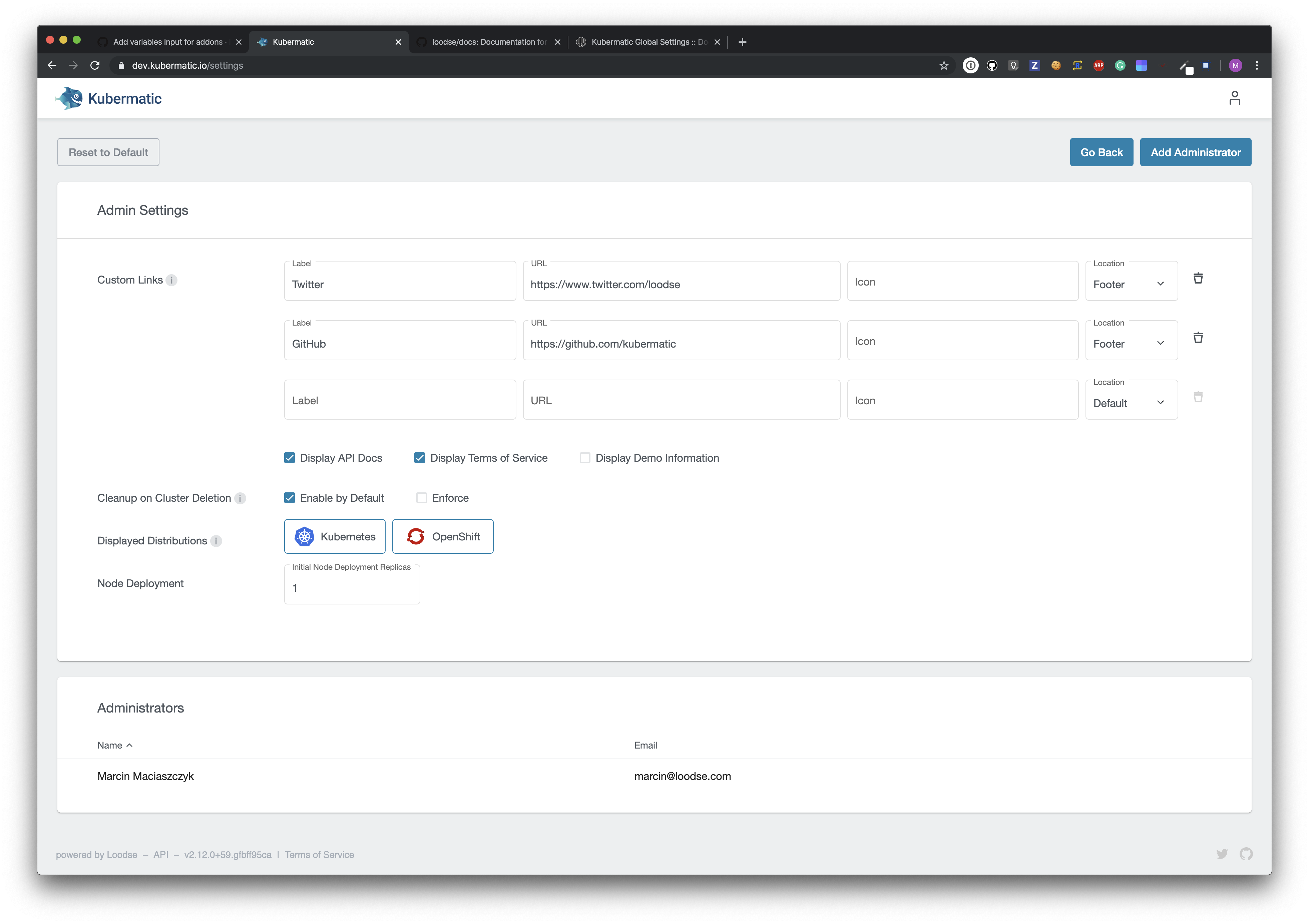
Admin panel consist of two cards. One allows to manipulate global settings, the second allows to manipulate the list of admin users. All settings changes are saved asynchronously, and the saves are confirmed by the green confirmation icons next to changed settings. Changes are automatically populated to all opened instances of the application.
Changing the Global Settings Using kubectl
Global settings are stored in KubermaticSetting custom resource named globalsettings.
The resource has following structure:
apiVersion: kubermatic.k8s.io/v1
kind: KubermaticSetting
metadata:
name: globalsettings
...
spec:
cleanupOptions:
Enabled: true
Enforced: false
clusterTypeOptions: 0
customLinks:
- icon: ""
label: Twitter
location: footer
url: https://www.twitter.com/kubermatic
- icon: ""
label: GitHub
location: footer
url: https://github.com/kubermatic
- icon: ""
label: Slack
location: footer
url: http://slack.kubermatic.io/
defaultNodeCount: 1
displayAPIDocs: true
displayDemoInfo: false
displayTermsOfService: true
It can be edited directly from the command line:
$ kubectl edit kubermaticsetting globalsettings
Note: Custom link icon is not required and defaults will be used if field is not specified. icon URL can
point to the images inside the container as well, i.e. /assets/images/icons/custom/github.svg.