This section describes how to add, create and manage Kubernetes clusters known as external clusters in KKP. You can create a new cluster or import/connect an existing cluster.
Import: You can import a cluster via credentials. Imported Cluster can be viewed and edited. Supported Providers:
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
- Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
Connect: You can also connect any cluster in the KKP via kubeconfig. Connected clusters can only be viewed, not edited.
The KKP platform uses the provided kubeconfig or generates a new one from the cloud provider API. The KKP backend takes advantage of this kubeconfig to retrieve the cluster’s information, nodes, metrics, and events. Every cluster update is performed only by the cloud provider client. There is no need to install any agent on the cloud provider side.
Prerequisites
The following requirements must be met to add an external Kubernetes cluster:
- The external Kubernetes cluster must already exist before you begin the import/connect process. Please refer to the cloud provider documentation for instructions.
- The external Kubernetes cluster must be accessible using kubectl to get the information needed to add that cluster.
- Make sure the cluster kubeconfig or provider credentials have sufficient rights to manage the cluster (get, list, upgrade,get kubeconfig)
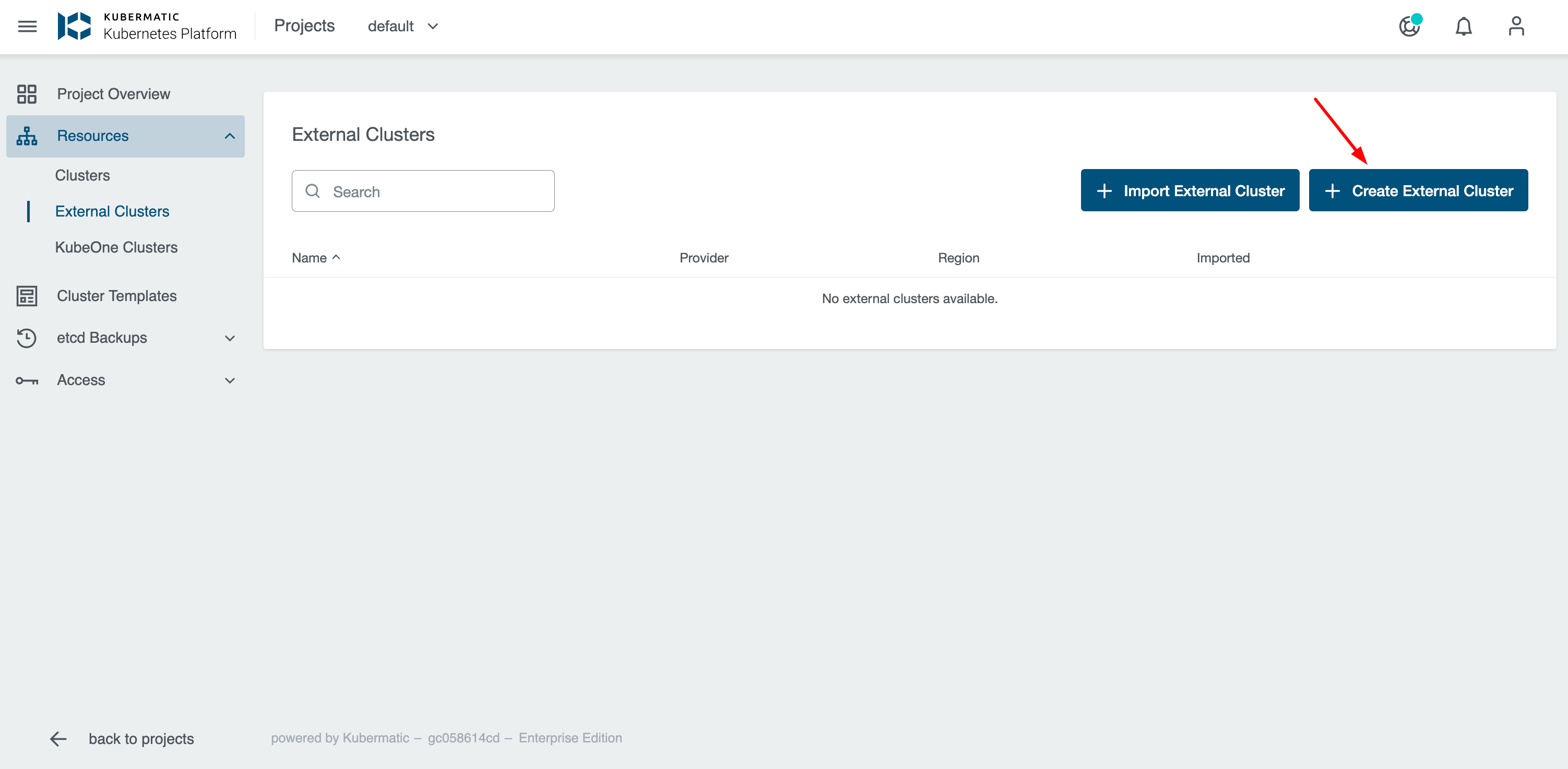
Import External Cluster
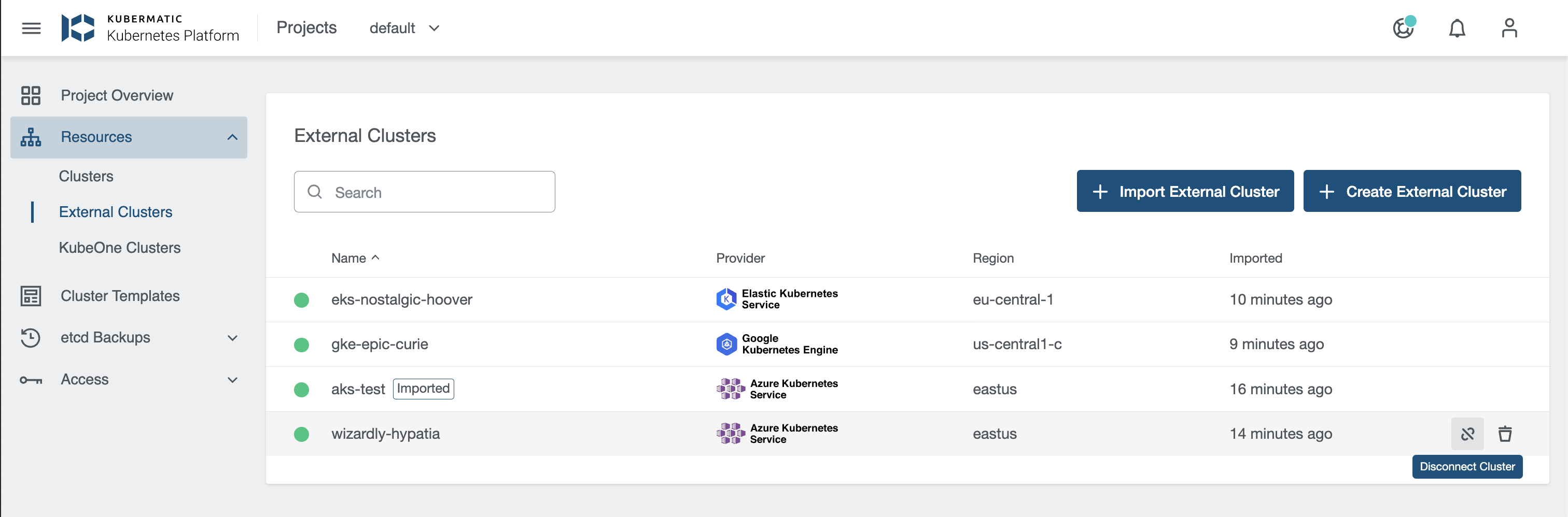
KKP allows connecting any existing Kubernetes cluster as an external cluster to view the cluster’s current state.
- To add a new external cluster go to
External Clusterspage and Click theImport External Clusterbutton.
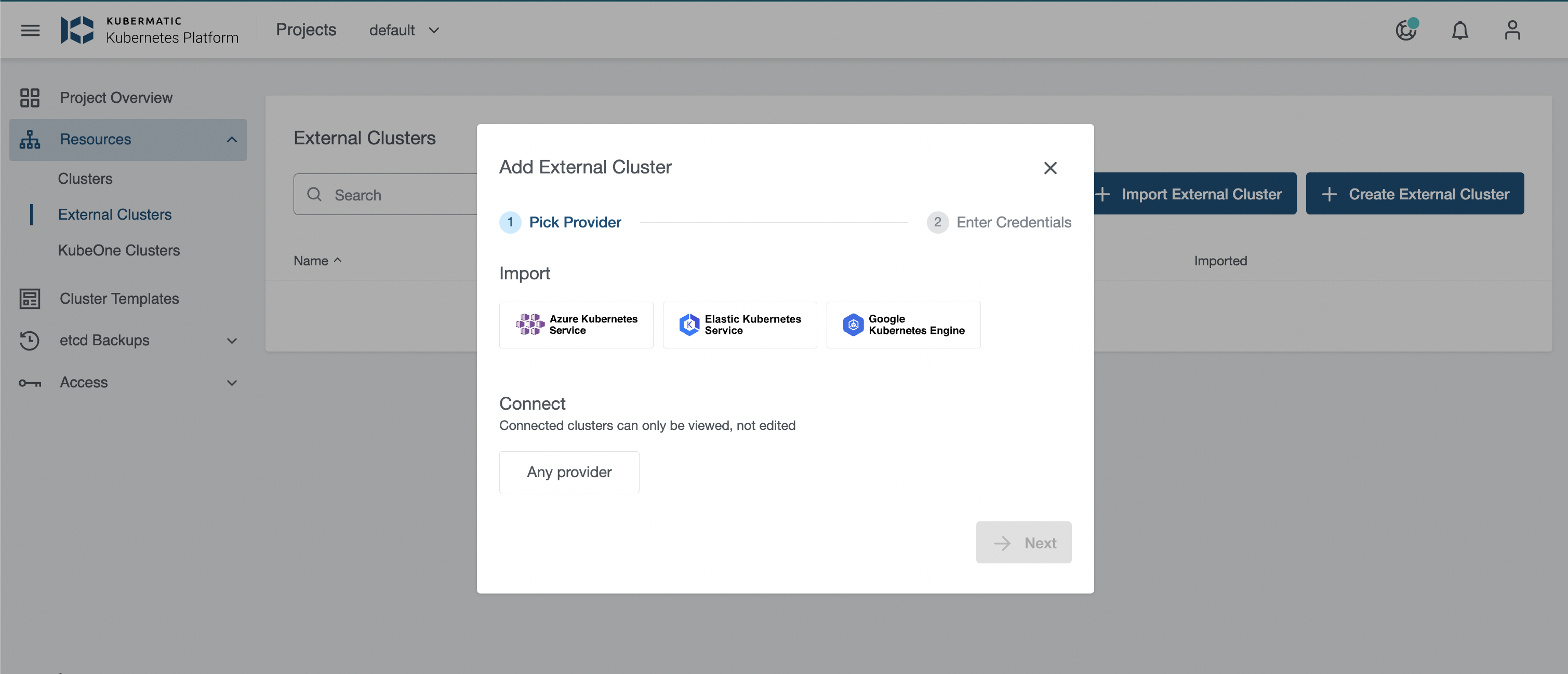
Select the Kubernetes cloud provider. You can add or create the following external clusters:
To connect a cluster from any provider, click on
Any Providerand provide the cluster name and kubeconfig.
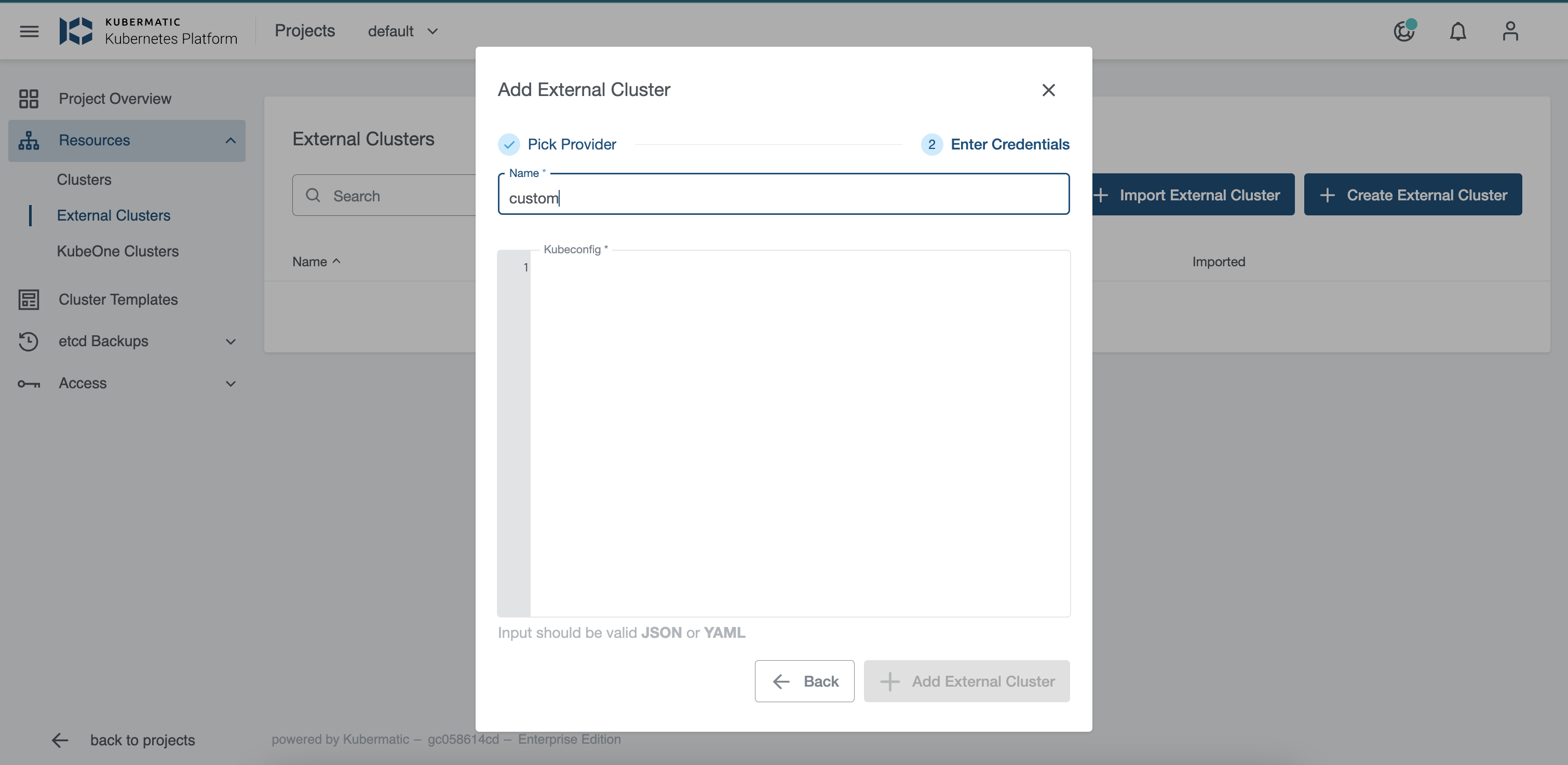
It is important that the kubeconfig used to connect the cluster is using standard authentication mechanisms like certificates or ServiceAccount tokens. OIDC or provider-specific plugins are not supported.
If an existing kubeconfig uses custom authentication mechanisms, kubermatic-installer convert-kubeconfig can (optionally) be used to create a ServiceAccount on the external cluster and fetch its token into a new kubeconfig.
You can then see the details of the cluster.
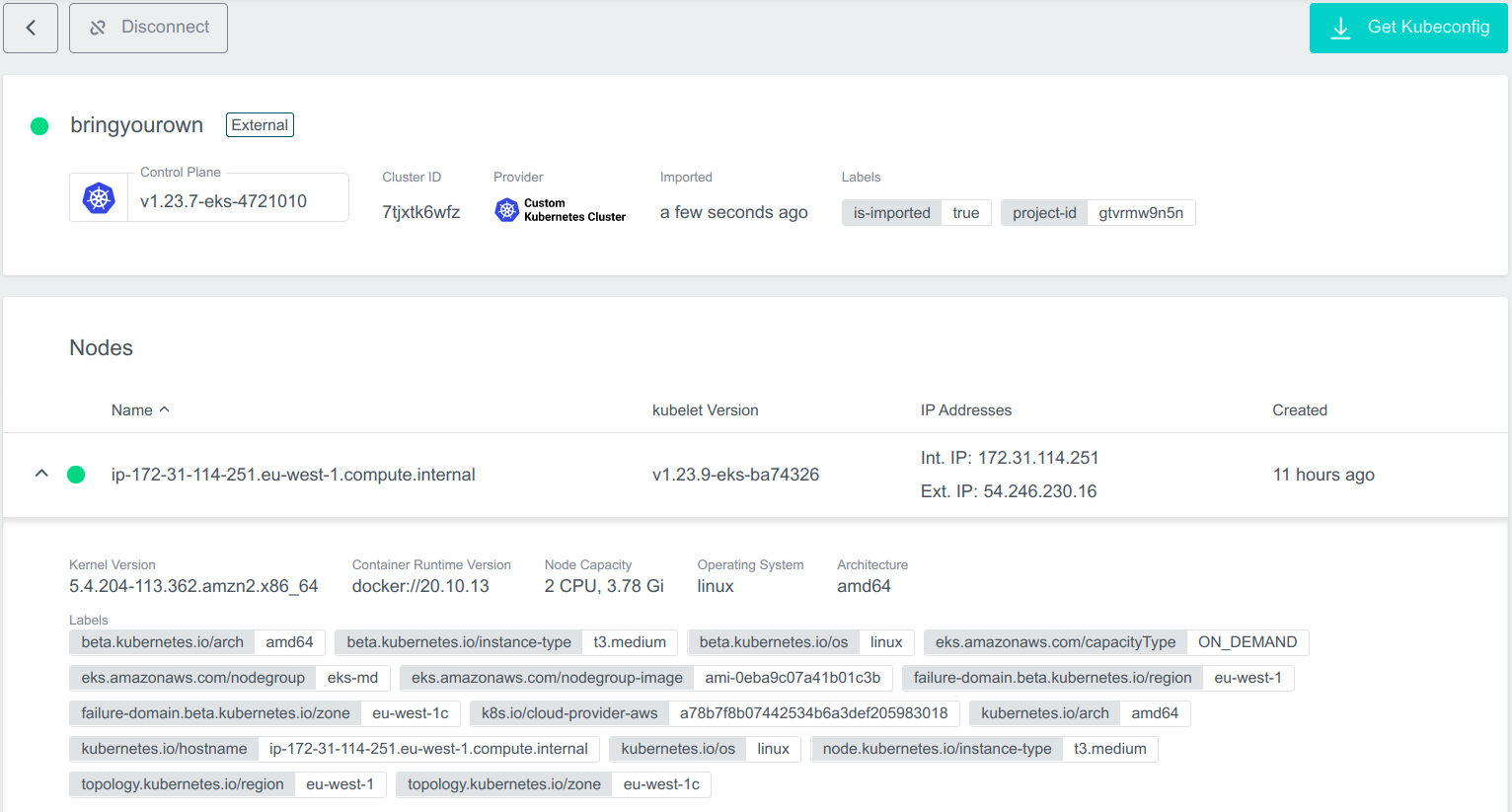
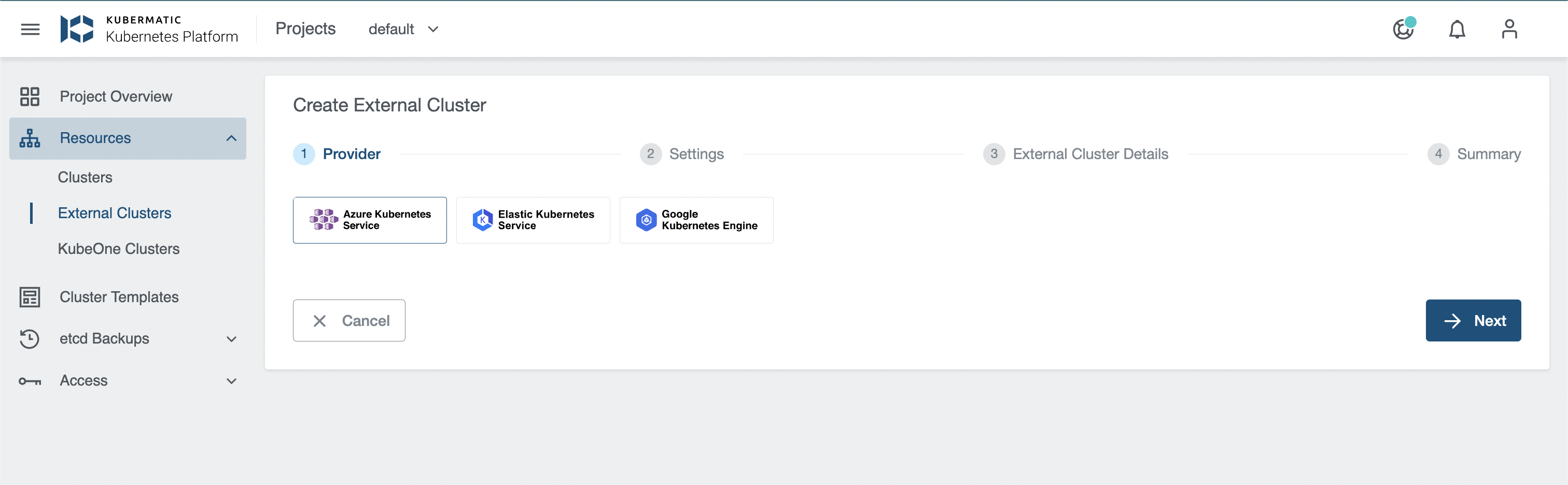
Create External Cluster
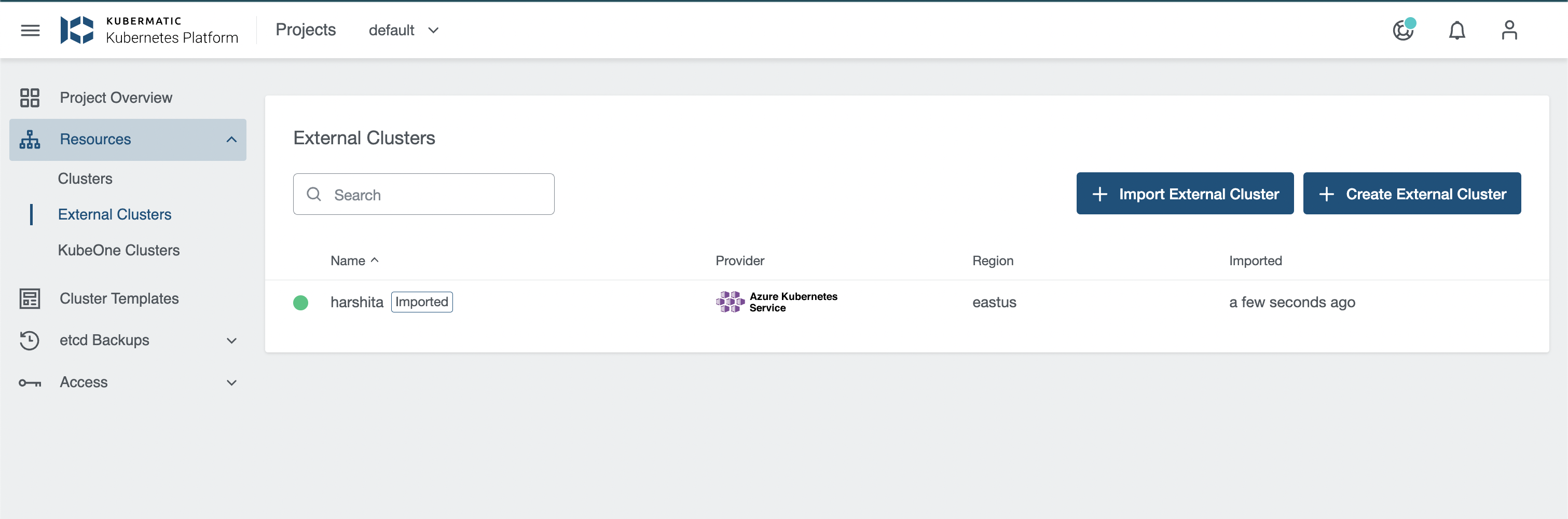
KKP allows creating a Kubernetes cluster on AKS/GKE/EKS and import it as an External Cluster.
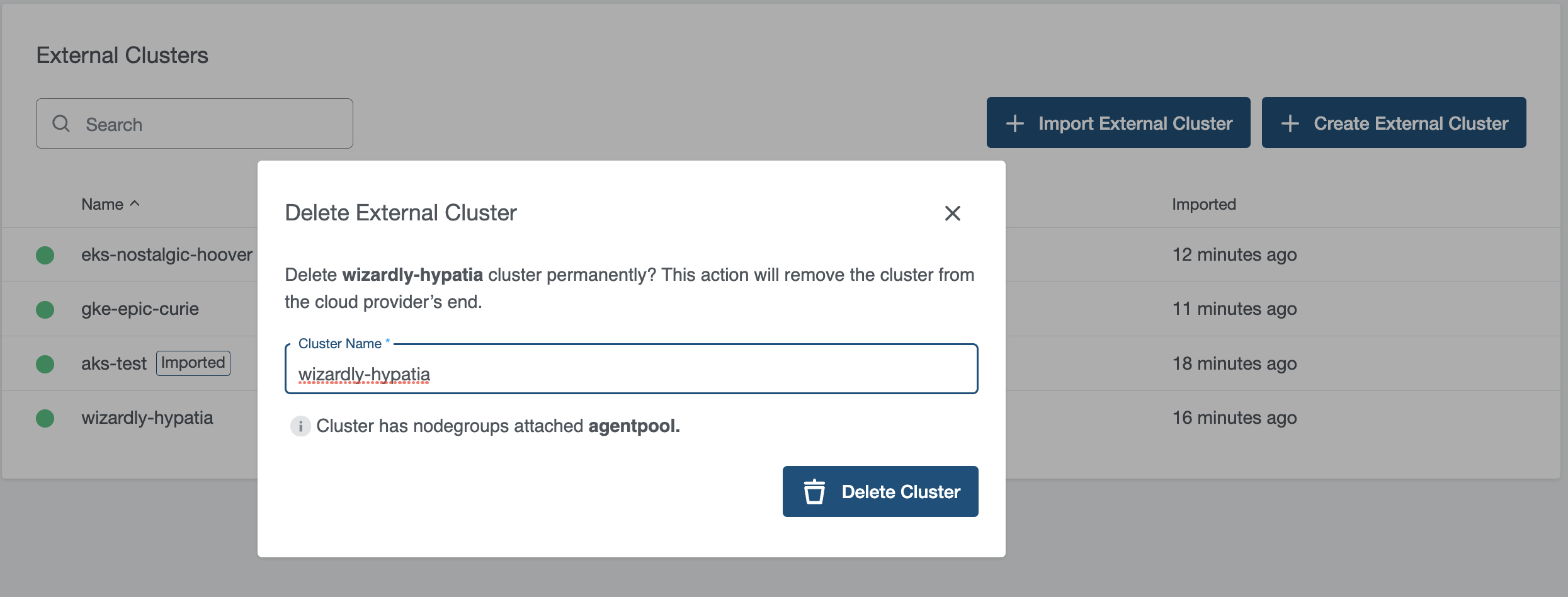
Delete Cluster
Delete operation is not allowed for imported clusters.
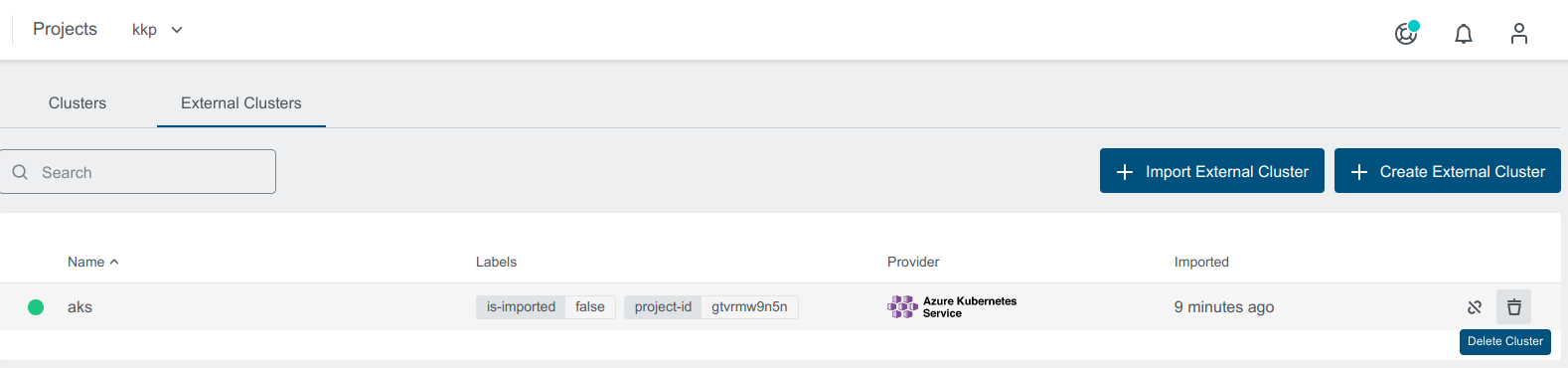
Cluster can be Deleted by clicking on the delete icon next to the cluster you want to delete or from the cluster details page, which will delete and disconnect the cluster from the provider.
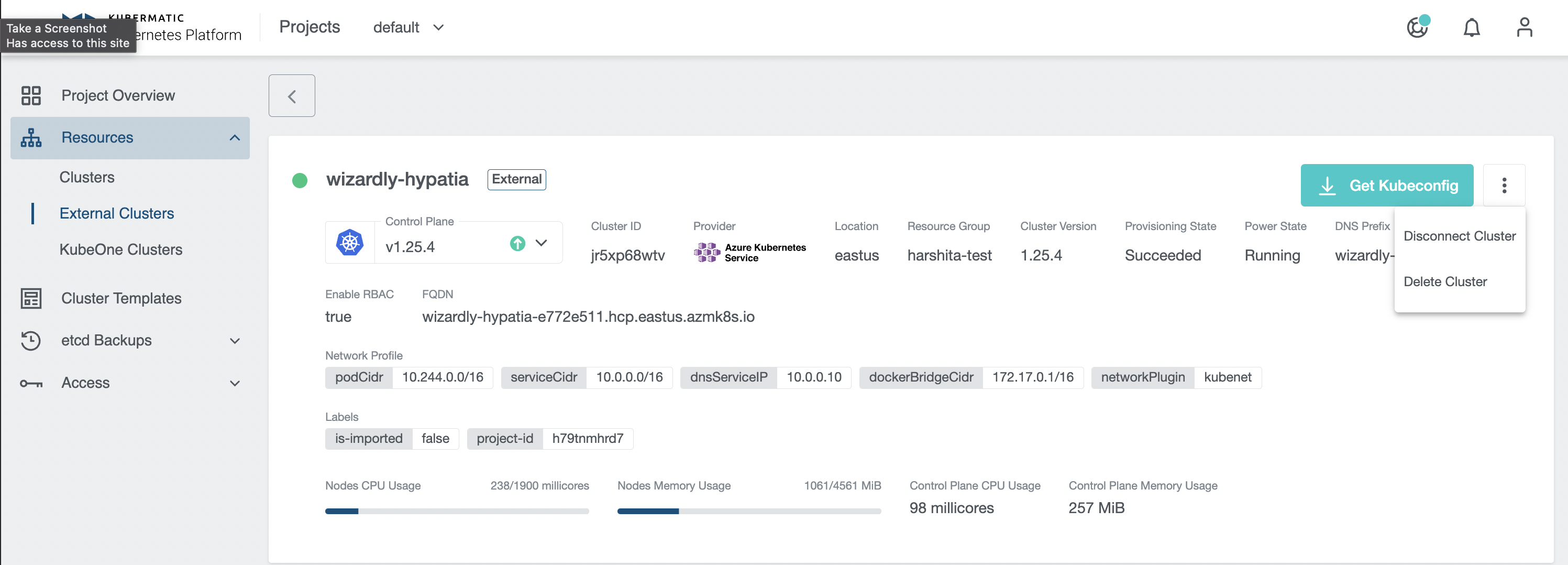
Cluster State
You can view the current state of your cluster by hovering the cursor over the small circle on the left of the cluster name.
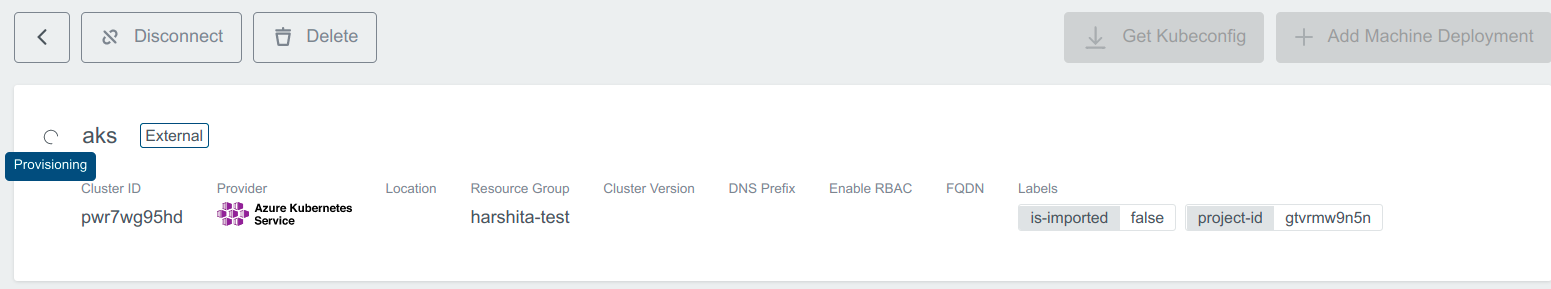
Provisioning state depicts that the cluster is getting created:
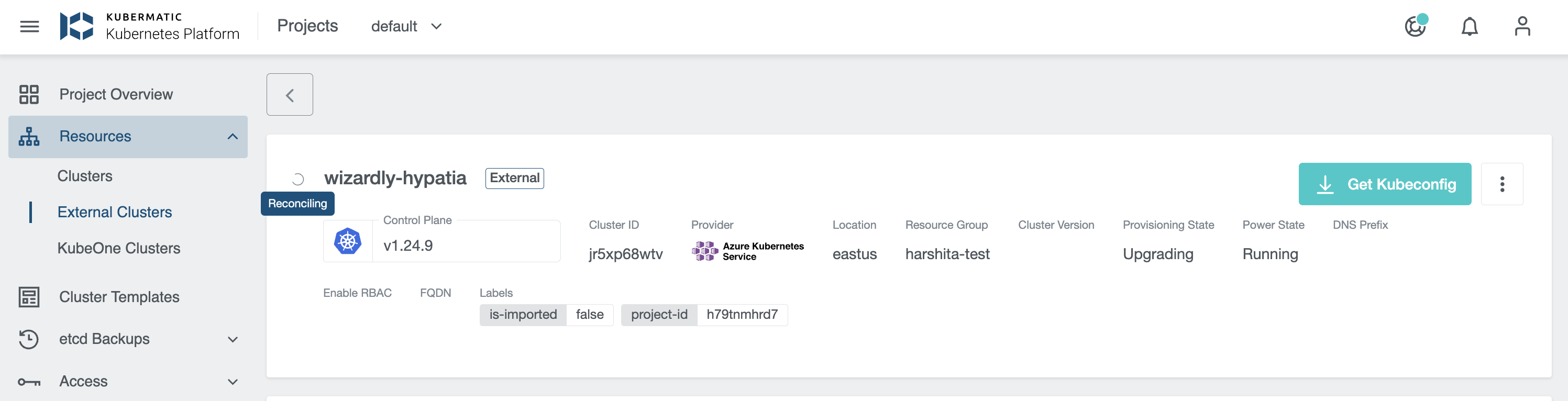
Reconciling state depicts that the cluster is getting upgraded:
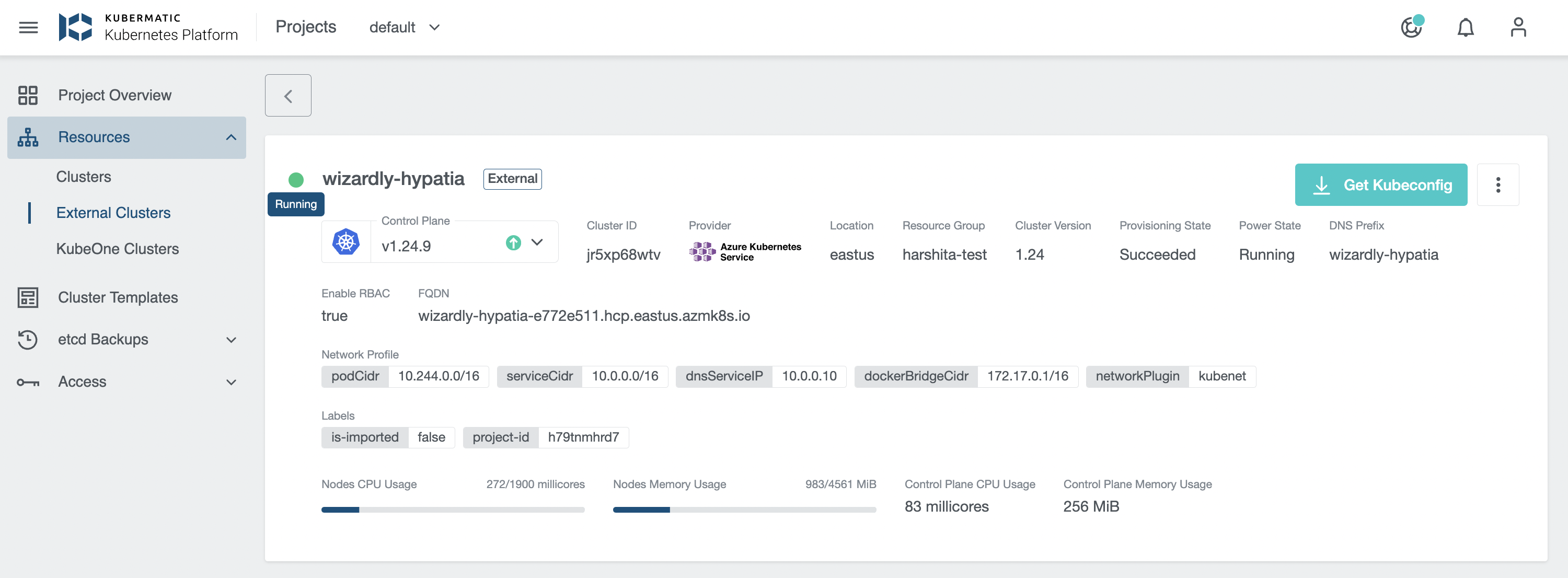
Running state depicts that the cluster is healthy:
Deleting state depicts that the cluster is getting deleted:
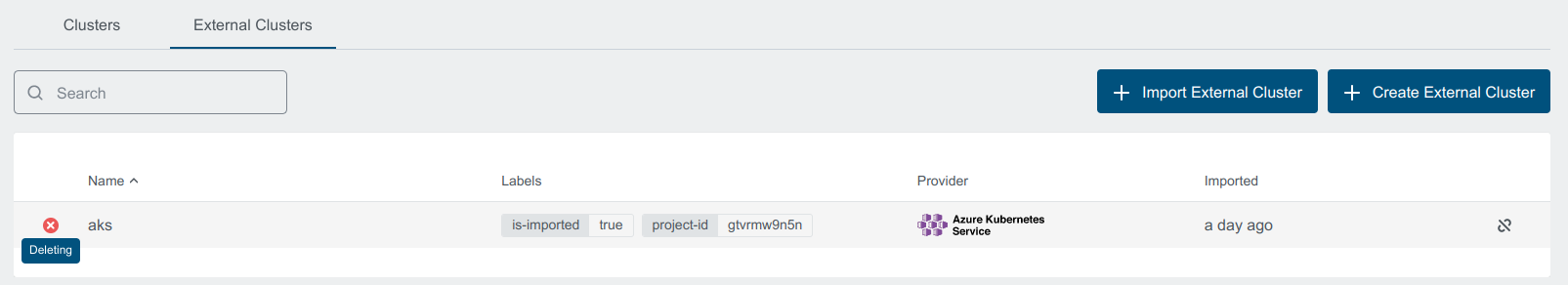
Disconnect Cluster
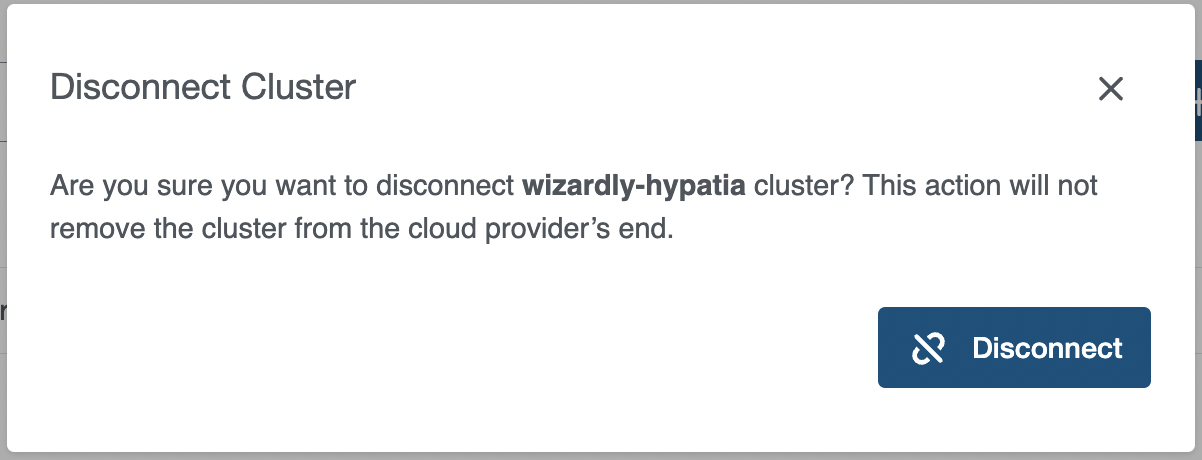
Disconnect operation does not delete the cluster from the cloud provider.
You can Disconnect an external cluster by clicking on the disconnect icon next to the cluster you want to disconnect or from the cluster details page, which will delete internal cluster object in KKP.
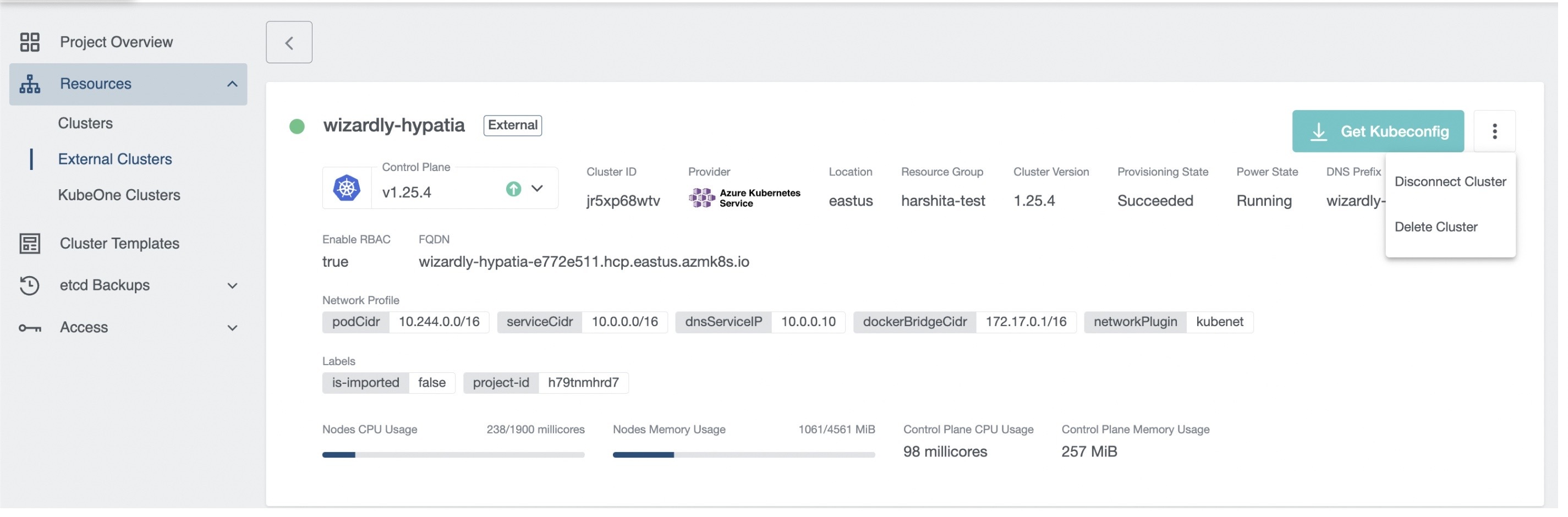
Delete Cluster
Delete Cluster displays information in case nodes are attached