KubeCarrier is a multi-tenant application service management platform (service hub) that runs across multiple Kubernetes clusters of two types: Management and Service clusters. The platform is managed and consumed by different types of actors: Platform Operators, Service Providers and Service Consumers.
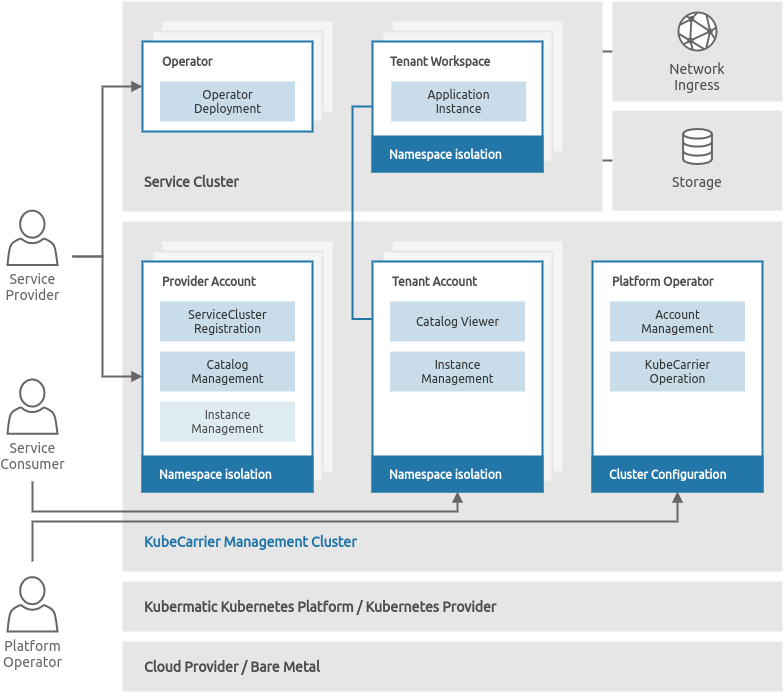
Cluster Types
Each KubeCarrier platform installation consists of two types of clusters: a Management Cluster and Service Clusters.
Management Cluster
As part of the KubeCarrier Installation, KubeCarrier operator is installed into a Kubernetes cluster. This cluster will become the Management Cluster, which will provide the central Service Hub functionality for management and distribution of applications running in one or more Service Clusters registered in the Management Cluster.
Service Clusters
Service Clusters are Kubernetes clusters that run the actual application workloads managed by their Kubernetes Operators, which are driven by the KubeCarrier Service Hub. To allow that, the Service Clusters first have to be registered in the Management Cluster.
Application Operators running in the Service Clusters are providing services via their Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs). After including of a CRD in a CatalogEntrySet, KubeCarrier will automatically discover that CRD in the registered Service Clusters, and make them available for management and distribution via the central Service Hub.
Whenever a new instance of a service’s Custom Resource (CR) is created in the Service Hub for a given Service Cluster, KubeCarrier will automatically propagate it into the target Service Cluster, which will drive the Operator running in it to deploy the application.
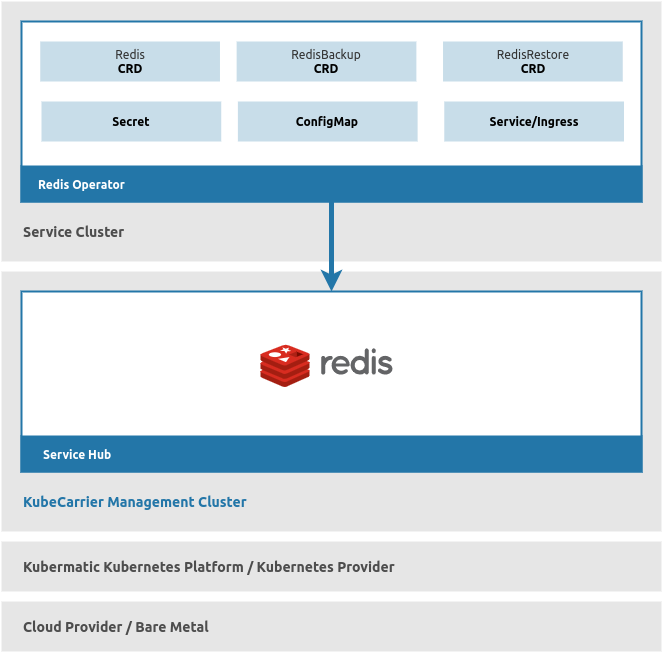
Example
As an example, take a look at the picture below. A Redis Operator that runs in a Service Cluster exposes
3 CRDs (Redis, RedisBackup, RedisRestore). These are included for management by KubeCarrier by creating
respective CatalogEntrySets
in the KubeCarrier Management Cluster. Since the Service Cluster is registered in the Management Cluster,
KubeCarrier will automatically discover those CRDs in the Service Cluster and make them available for consumption
in the Catalog of the Service Hub.
Whenever a new instance of a Redis CRD is created in the Service Hub for the given Service Cluster, KubeCarrier will automatically propagate it into the Service Cluster, which will drive the Redis operator in it to perform action (e.g. deploy a new Redis instance with all respective Secrets, ConfigMaps, Services, etc. in the tenant namespace).
Actors
The KubeCarrier platform is managed and consumed by different types of actors: Platform Operators, Service Providers and Service Consumers.
Platform Operator
The Platform Operator is responsible for the management of the KubeCarrier infrastructure - KubeCarrier Management Cluster itself, as well as the KubeCarrier installation and setup in it, including management of KubeCarrier Accounts.
Service Provider
The Service Provider is responsible for making an application services available in the Service Hub and all their day 2 operations. That includes:
- management / registration of KubeCarrier Service Clusters,
- deployment / management of Kubernetes Operators running in the Service Clusters,
- management of CatalogEntrySets and Catalogs (instance management).
Service Consumer
The Service Consumers care only about the deployment and configuration of the desired application services. They can do it by creation of an application Custom Resource in a Tenant namespace of the Management Cluster. That will result in application running in a Tenant namespace of the Service Cluster, where the Service Consumer does not need to have any access.
Multi-Tenancy
KubeCarrier provides out-of-the-box multi-tenancy support via Accounts. Each Account is separated by its own Kubernetes Namespace and subjects within the Account get proper Kubernetes RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) Roles setup and assigned automatically.